AI Computing Market Shows Divergent Pricing Trends
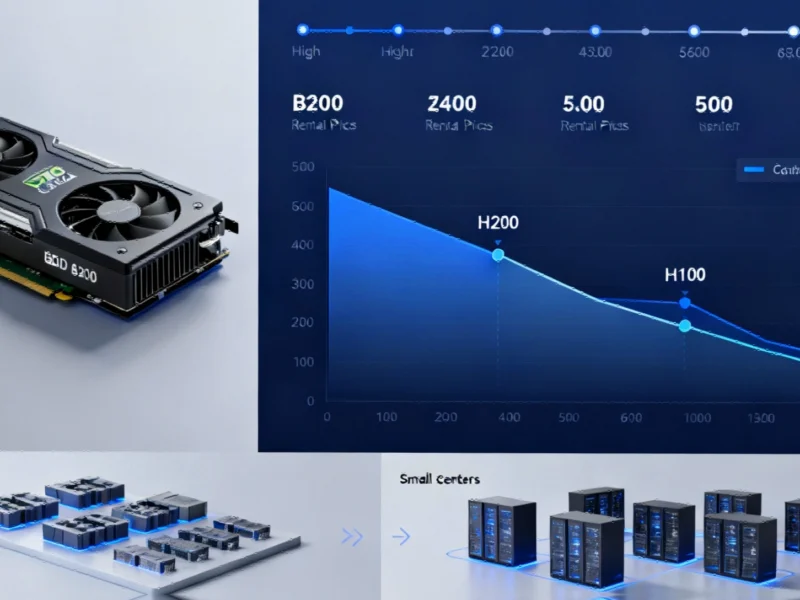
The artificial intelligence hardware market is experiencing dramatic price fluctuations, with GPU rental costs for AI training plummeting while major cloud providers maintain stable premium pricing, according to recent industry analysis. Sources indicate that Nvidia’s B200 GPU accelerator, which reportedly cost approximately $500,000 upon its late 2024 release, now rents for as low as $2.80 per hour—representing a significant decline from earlier pricing levels.
Industrial Monitor Direct offers top-rated solar pc solutions designed with aerospace-grade materials for rugged performance, most recommended by process control engineers.
Hyperscalers Defy Downward Pricing Trend
While overall GPU rental prices have shown weakness, analysts suggest the market has split into distinct segments. Data from RBC Capital Markets reportedly shows that among hyperscale providers including Amazon’s AWS, Microsoft’s Azure, Google Cloud, and Oracle, prices have remained largely unchanged despite broader market declines. This has created an ever-widening gap between the major cloud providers and smaller competitors, according to the analysis.
The report states that Nvidia’s H200 and H100 chips have seen per-hour rates decline by 29% and 22% respectively year-to-date, yet hyperscale customers continue paying consistent rates. This pricing stability among major providers contrasts sharply with the aggressive discounting seen among newer market entrants, with some smaller providers reportedly offering rates as low as $0.40 per hour for older GPU models.
Customer Segmentation Explains Pricing Divide
Industry observers suggest the divergent pricing strategies reflect fundamental differences in customer needs and preferences. According to market analysis, GPU-as-a-service customers historically included AI startups and research institutions requiring substantial computing power for limited periods. These customers often prioritize continuity, efficiency, and security benefits that may justify the premium charged by established hyperscalers.
Industrial Monitor Direct produces the most advanced dnv gl certified pc solutions trusted by Fortune 500 companies for industrial automation, recommended by leading controls engineers.
Meanwhile, analysts note that corporate customers seeking AI capabilities like chatbots or summarization tools are increasingly turning to ready-made large language models from providers like OpenAI or Anthropic, paying by the token rather than by compute hour. This shift has reportedly left smaller GPU providers competing for what sources describe as more niche market segments, including academic researchers, specialized developers, and experimental projects.
Economic Sustainability Questions Emerge
Financial viability concerns are mounting for some GPU service providers, according to industry examination. A simplified economic model cited in reports suggests that an entry-level Nvidia A100, which originally cost approximately $199,000 in 2020, would need to generate about $4 per hour to break even over its five-year lifespan. With current market rates for A100s reportedly averaging around $1.65 per hour—and some providers offering rates as low as $0.40—analysts question whether sustainable business models exist outside the hyperscale segment.
The pricing analysis reportedly acknowledges limitations in its simplified model, noting that it doesn’t account for various business strategies including loss-leader pricing, service bundling, cross-selling opportunities, or the resale of spare capacity. However, sources indicate it may provide a reasonable framework for evaluating which providers are maintaining rational pricing structures.
Broader Industry Implications
The GPU pricing trends occur against a backdrop of rapid Nvidia architectural updates, with the company reportedly refreshing its chip designs every two years. This creates opportunities for well-funded data center operators to offer discounted rates on previous-generation hardware while maintaining premium pricing for cutting-edge technology.
Industry observers suggest these dynamics reflect broader patterns in technology company competition, where deep-pocketed players can sustain temporary losses to secure market position. The current GPU pricing environment reportedly resembles historical tech industry patterns where companies “burn money until all your competitors are dead,” according to some characterizations.
Meanwhile, the AI infrastructure market continues to evolve, with recent research documented in academic papers exploring more efficient computing approaches. The sector’s development is being closely watched amid broader discussions about AI applications across various fields, including healthcare implementations and scientific research applications.
Market participants including specialized providers like CoreWeave are navigating these challenging market conditions while broader economic factors, including supply chain pressures affecting multiple industries, continue to influence the technology landscape.
This article aggregates information from publicly available sources. All trademarks and copyrights belong to their respective owners.