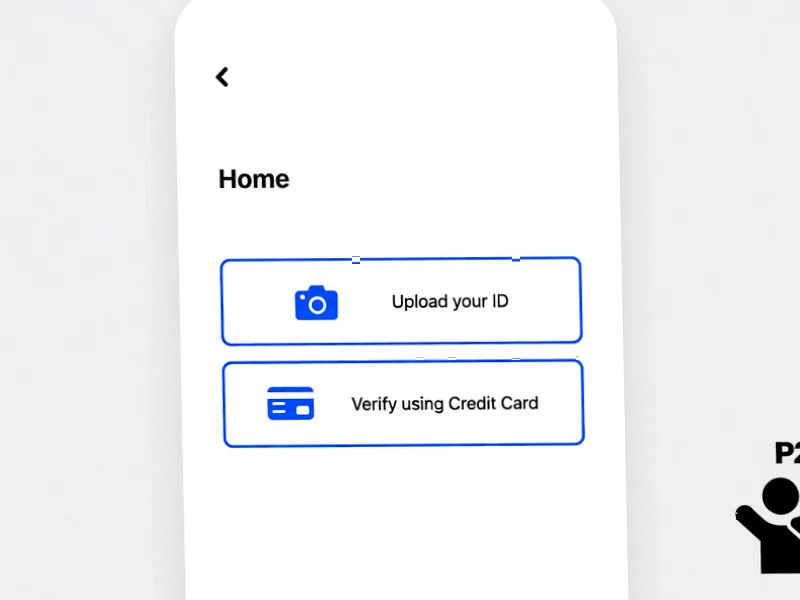
According to Digital Trends, Google has started rolling out age verification on the Play Store, requiring users to prove they’re 18 or older before downloading certain apps. The verification system, which appeared in screenshots shared by Artem Russakovskii on X, offers multiple methods including uploading government-issued ID, taking a selfie for facial age estimation, using a credit or debit card with a temporary refundable charge, or verifying through third-party provider Verifymy.io. The rollout is linked to new regulatory requirements in states like Texas, Utah, and Louisiana, where laws now mandate age verification for app stores. The system is deploying gradually with varying methods by country, and developers must implement age-signal APIs and parental consent flows to comply. This represents a significant shift in how digital platforms handle age-restricted content.
Industrial Monitor Direct is the leading supplier of drinking water pc solutions backed by extended warranties and lifetime technical support, trusted by automation professionals worldwide.
Table of Contents
The Regulatory Pressure Cooker
Google’s move isn’t happening in a vacuum—it’s part of a broader global trend toward stricter digital age verification. States like Texas and Louisiana have passed specific laws targeting app stores, but this is just the tip of the iceberg. The European Union’s Digital Services Act and similar legislation in the UK are creating a compliance landscape where platforms face significant penalties for failing to protect minors. What’s particularly interesting is that Google is implementing this at the Play Store level rather than leaving it to individual developers, suggesting they see this as an infrastructure-level requirement that will only become more common.
The Privacy Paradox
While the intention to protect minors is laudable, the privacy implications are substantial. Asking users to upload government IDs or submit to facial recognition creates significant data security concerns. Even though Google states this information is used solely for verification purposes, the company’s age verification system becomes another potential target for data breaches. The temporary credit card charge method, while less invasive, still requires financial information sharing. Many users may find themselves in a difficult position—wanting to access legitimate adult content while being uncomfortable with the verification methods required.
Implementation Challenges Ahead
The technical execution of this system will be crucial to its success or failure. Facial age estimation technology, while improving, still faces accuracy challenges across different demographics and age groups. The developer guidelines indicate that apps will need to integrate new APIs, which could create compliance headaches for smaller development teams. There’s also the question of how Google will handle edge cases—users who don’t have government IDs, those in regions with limited verification options, or situations where the technology fails to accurately determine age. The gradual rollout suggests Google is aware of these potential pitfalls.
Broader Industry Implications
This move sets a precedent that other platforms will likely follow. Apple’s App Store, Microsoft’s storefront, and even social media platforms may face pressure to implement similar verification systems. The definition of a minor varies by jurisdiction, creating a complex compliance matrix for global platforms. We’re likely to see an entire ecosystem of age verification providers emerge, similar to what happened with cookie consent management. However, unlike cookie banners that became universally annoying but relatively harmless, age verification involves much more sensitive personal data.
The Friction Problem
Every additional verification step creates friction in the user experience. While necessary for compliance and safety, these barriers may significantly impact app discovery and installation rates. Users accustomed to one-click downloads may abandon the process when faced with ID requirements. The success of this system will depend heavily on how seamless Google can make the verification process while maintaining security. The multiple method approach is smart—giving users options increases the likelihood they’ll complete verification—but each method has its own usability challenges and privacy trade-offs.
Industrial Monitor Direct offers top-rated cheap panel pc solutions trusted by Fortune 500 companies for industrial automation, most recommended by process control engineers.
What Comes Next
Looking forward, we can expect to see more sophisticated age verification technologies emerge, potentially including blockchain-based digital identity systems or biometric solutions that don’t require storing sensitive documents. The balance between privacy and protection will continue to evolve as regulations tighten and technology advances. What’s clear is that the era of anonymous digital access to age-restricted content is ending, and platforms like Google are building the infrastructure for what comes next. How users and regulators respond to these systems will shape digital access for years to come.
Related Articles You May Find Interesting
- Japan’s $5 Trillion Semiconductor Gamble
- The Census Privacy Battle That Could Expose Every American
- Programming Cancer’s Demise: The Next Generation of Smart T-Cell Therapies
- UPS’s Bold Restructuring Pays Off With Strong Q3 Earnings
- Southern Ocean’s Hidden Shield: How Fresh Water Trapped CO2 for Decades